Vault Quickstart
CS Vault Quickstart Guide
This guide will give you an introduction to using the Computer Science vault. We will show you how to do things both in the web interface and through command line access.
Introduction
The CS vault is a secrets store based on Hashicorp Vault https://www.vaultproject.io/ It allows you to securely store secrets such as passwords, certificates, and private keys. The data is stored encrypted and transmitted encrypted. It is all API driven, so can be integrated easily into your applications.
Authentication
All access to the CS vault is made through temporary tokens. Generally you do not personally use a token to log into the service unless you are directly access the API. Either the vault agent command line or the web interface will manage the temporary tokens for you once you log in with another method.
- We offer multiple authentication methods
- Each method logs in you into a separate identity that will have separate access levels even if the username is the same. For example, "carnold" logged in through CAS is not the same as "carnold" logged into through LDAP.
CAS
Using CAS login is the easiest way to log into the CS vault website https://vault.enterprise.cs.vt.edu
- Select
castab from the login screen - Click on "Sign in with OIDC Provider" and another window will open with CS CAS Login if needed.
- CAS login can be used with command line interface as well
vault login -method=cas- It will give a URL that you need to open in a browser to finish the login
LDAP
You can use traditional CS username/password to log into CS Vault through the web interface or the command line interface.
- LDAP is best suited for command line interface
- Vault policies can be applied to your LDAP login based on your LDAP group memberships -- for example a shared group secrets path
AppRole
We also provide Vault's AppRole authentication. Find out more about AppRole: https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/auth/approle
- This method is meant as a systematic way for applications to access the vault API
- Techstaff will have to create a unique AppRole login for each of your applications and apply policies based on your specific needs.
- We recommend you use vault agent to manage your App's access to vault, this will greatly reduce the complexity of your application. See: https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/agent
Web Interface
Using the CS Vault web interface is the quickest and easiest way to get started using CS Vault.
- https://vault.enterprise.cs.vt.edu
- You can log into the web interface using any of the supported authentication methods
Command Line Interface
Vault offers a command line interface. You will need to download a binary for your system to run it.
- Download: https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/downloads
- You will need to tell the vault command line which vault server to connect to either through a command line option or environment variable
- Example:
export VAULT_ADDR=https://vault.enterprise.cs.vt.edu vault login -method-ldap username=carnold vault list personal/carnold
- By default the command line will store the token at
~./vault-token - You can effectively logout by removing the stored token:
rm ~/.vault-token - More information about the vault command line: https://developer.hashicorp.com/vault/docs/commands
Example: Personal Vault
The CS vault by default will give you access to a personal secrets path at /personal/<username> You can store any Key/Value items in this personal vault.
From Web Interface
- Click on the Secrets tab at the top
- Click on personal from the secrets list
- Click on Create secret to create a new secret
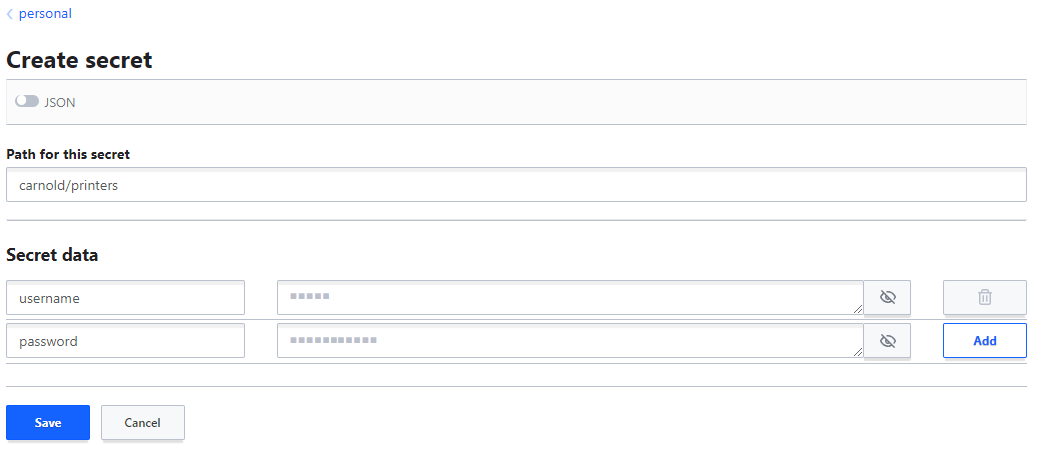
- Fill in Path for this secret with
<username>/<my-secret-name>Example:carnold/printers - Fill in Secret data with any number of key = value pairs you want. The key is displayed in clear text and the value is kept secret.
- Click on Save